Hookworm: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Hookworm is a common parasitic infection caused by several species of nematodes (roundworms) that typically inhabit the intestines of their hosts. While often associated with poor sanitation and hygiene, hookworm infections can occur worldwide and affect humans and animals alike.
Understanding Hookworm
What is Hookworm?
Hookworm refers to parasitic nematodes that inhabit the intestines of humans or animals. The name "hookworm" is derived from the hook-like mouthparts they use to attach to the host's intestinal wall. Common species in humans include Ancylostoma duodenale and Necator americanus.
Life Cycle and Transmission
Hookworms have a direct life cycle. The adult worms reside in the intestines and lay eggs that are passed in the host's feces. In optimal environmental conditions (warm, moist soil), these eggs hatch into larvae. Humans or animals contract hookworm by walking barefoot on contaminated soil, as the larvae penetrate the skin and migrate to the intestines via the bloodstream and respiratory system.
Who is at Risk?
Anyone can get hookworm, but those with increased risk include:
- People living in tropical or subtropical regions.
- Individuals with poor sanitation and inadequate sewage systems.
- Those who frequently walk barefoot on contaminated soil.
How Common is Hookworm?
Approximately 575-740 million people worldwide are infected with hookworm. It is prevalent in areas with warm climates and poor sanitation.
Symptoms and Causes
What are the Signs of Hookworm Infection?
Many people with hookworm are asymptomatic. However, symptoms can arise depending on the severity of the infection:
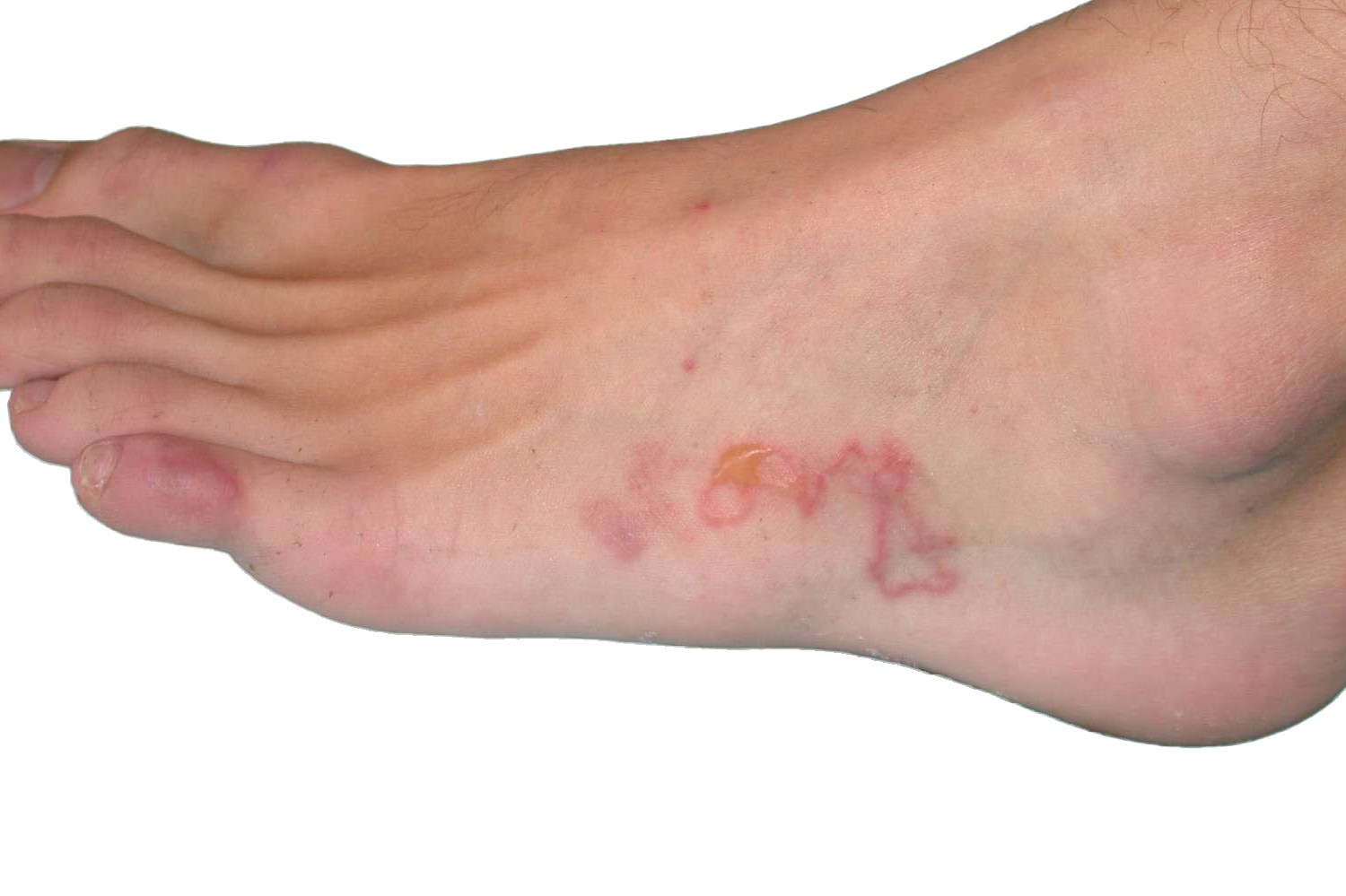
- Itchy Rash (Ground Itch): Soon after larvae penetrate the skin.
- Abdominal Pain: Often crampy, and associated with nausea.
- Diarrhea or Constipation: Altered bowel habits.
- Anemia and Fatigue: Due to blood loss from worms feeding on host's blood.
- Protein Deficiency: Severe infections can lead to nutritional deficiencies.
What Causes Hookworm?
The primary cause of hookworm infections is exposure to environments contaminated with hookworm larvae, especially when proper hygiene and sanitation measures are lacking.
Diagnosis and Tests
How is Hookworm Diagnosed?
Diagnosis often involves the examination of stool samples for the presence of hookworm eggs. In cases with low worm burdens, multiple samples may be needed to confirm the infection:
- Microscopic Examination: Of stool specimens to detect eggs.
- Blood Tests: May show anemia or eosinophilia, indicating parasitic infection.
- Skin Examination: Inflamed areas known as "ground itch" can be indicative.
Additional Resources:
Management and Treatment
How is Hookworm Treated?
Treatment primarily focuses on eliminating the parasites and correcting any nutritional deficiencies:
Anthelmintic Medications
Prescription antiparasitic drugs are essential:
- Albendazole: 400 mg single dose Drug Information
- Mebendazole: 100 mg twice daily for three days Drug Information
Iron Supplements
For those with anemia, oral iron supplements are often prescribed to restore normal blood levels.
Home Remedies and Prevention
Improving sanitary conditions and adopting hygiene practices significantly curtail hookworm transmission:
- Avoid walking barefoot in areas prone to hookworm.
- Use proper sanitation facilities.
- Avoid contact with contaminated soil or fecal matter.
Prevention
How Can I Prevent Hookworm?
Preventive measures revolve around improving sanitation and personal hygiene:
- Wear shoes outdoors in endemic areas.
- Ensure the presence of adequate and clean bathroom facilities.
- Regular deworming of pets and livestock.
Educational Resources
Living With Hookworm
When Should I Call the Doctor?
Consult your healthcare provider if you experience persistent abdominal pain, unexplained weight loss, or signs of anemia. These symptoms necessitate prompt investigation and treatment.
Questions to Discuss With Your Doctor
- How did I become infected with hookworm?
- What are the best practices to avoid future infections?
- Are family members at risk and should they be tested or treated?
- How soon after treatment will symptoms improve?
By following the guidance of healthcare professionals and implementing preventive measures, hookworm infections can be managed effectively, preventing complications and promoting better overall health.
Identify Skin Conditions Instantly
Try Rash ID for Free