Overview
Tinea cruris, more commonly known as jock itch, is a fungal infection that affects the skin in your groin, inner thighs, and sometimes the buttocks. It's caused by a type of fungus called dermatophytes, which are tiny organisms that can live on the outer layer of your skin.
These fungi thrive in warm, moist environments. Jock itch often develops when you sweat a lot or if the groin area stays damp for extended periods. While anyone can get jock itch, it's most commonly seen in adult men and adolescent boys, especially those who are active, sweat heavily, or are overweight. Yes, jock itch is contagious. It can spread through direct skin-to-skin contact or by sharing contaminated items like towels or clothing. Living with the persistent itch and discomfort of jock itch can be frustrating and sometimes embarrassing, but understanding it is the first step to feeling better.
Symptoms
You might be experiencing jock itch if you notice some of the following:
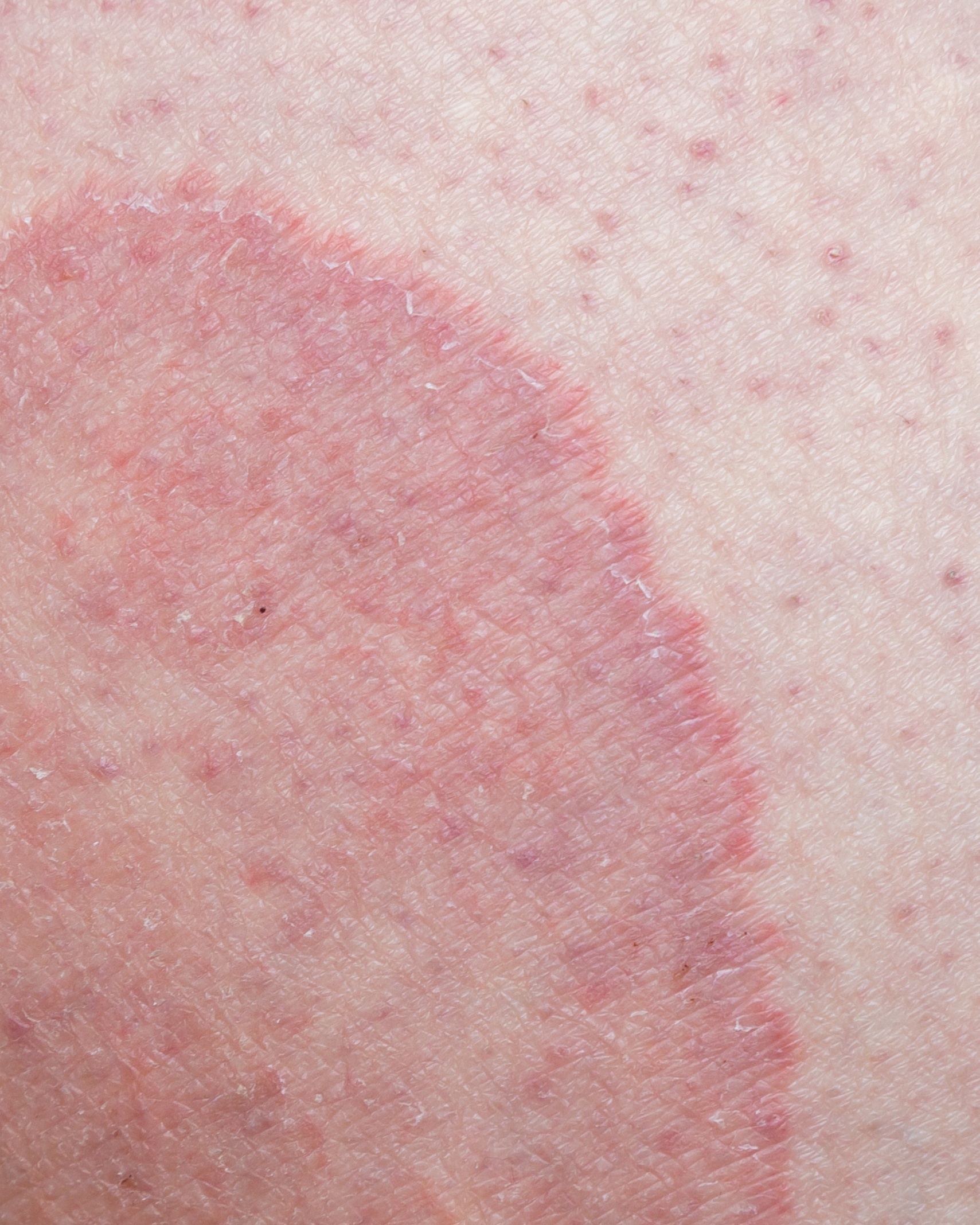
- A red, itchy rash - often in a half-moon or ring shape, in the groin, inner thighs, or on the buttocks.
- The edges of the rash - are typically raised, well-defined, and may be scaly or have small blisters.
- The skin in the center of the rash - might appear clearer or have a slightly different color, sometimes reddish-brown.
- Persistent and sometimes intense itching - in the affected area.
- A burning or stinging sensation - especially if the skin is irritated from scratching.
- Flaking, peeling, or cracking skin - in the affected region.
- The rash may feel worse or spread - after exercising or sweating.
- Sometimes, the skin can become irritated and more uncomfortable - if you scratch it a lot.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing jock itch usually starts with a visit to your healthcare provider. They will likely ask about your symptoms and medical history, and then carefully examine the rash. The characteristic appearance and location of the rash are often enough for a diagnosis.
In some cases, to confirm it's a fungal infection and not something else, your doctor might gently scrape a small sample of skin from the affected area. This painless procedure involves collecting a few skin cells, which are then looked at under a microscope or sent to a lab to check for the presence of fungi. This is often called a KOH test.
Management & Treatment
Dealing with the itch and irritation of jock itch can be frustrating, but the good news is that it’s usually easy to treat and manage at home. The goal is to eliminate the fungus and keep the area clean and dry to prevent it from coming back.
Most cases of jock itch can be effectively treated with over-the-counter (OTC) antifungal products. Look for creams, powders, or sprays containing ingredients like:
- Miconazole
- Clotrimazole
- Terbinafine
- Ketoconazole
Apply the treatment to the affected area as directed on the package, usually once or twice a day for two to four weeks. It's very important to continue using the medication for the full recommended time, even if your rash seems to be gone. Stopping too early can allow the infection to return.
In addition to medication, good self-care is key:
- Wash the groin area daily with soap and water, and dry it thoroughly with a clean towel.
- Wear loose-fitting clothing and choose underwear made of cotton or moisture-wicking synthetic fabrics.
- Change your underwear daily, or more often if you get sweaty.
- If you also have athlete's foot, put your socks on before your underwear to avoid spreading the fungus from your feet to your groin.
If the rash is severe, covers a large area, or doesn't start to improve after a couple of weeks of using an OTC product, it's time to see a healthcare professional. They may prescribe a stronger, prescription-strength antifungal cream or, in some cases, an oral antifungal medication.
Important Warning: Avoid using steroid creams, such as hydrocortisone, on the rash. While they might temporarily reduce the redness and itch, they can actually make the fungal infection worse and harder to treat.
Duration & Outlook
The good news is that jock itch typically responds well to care, and you might start seeing improvement within a few days to a week. With consistent attention, it often clears up within 2 to 4 weeks. Jock itch is usually an acute condition, meaning it comes on and resolves in a relatively short period.
However, if it's not managed properly, or if you're prone to it, jock itch can sometimes linger or come back. The expected outcome is usually complete resolution of the rash and itching. It's important to watch for warning signs of complications, such as the rash spreading rapidly, becoming very painful, oozing pus (which could indicate a bacterial infection), or if it doesn't improve with initial care.
Prevention
Preventing jock itch largely comes down to keeping the groin area clean and dry, and reducing friction.
- Wash your groin area daily - with soap and water, and dry it thoroughly, especially after showering, swimming, or exercising.
- Change your underwear - at least once a day, or more often if you sweat heavily.
- Wear loose-fitting clothing - and underwear made of breathable fabrics like cotton. This helps reduce moisture buildup and friction.
- Avoid sharing personal items - like towels, athletic supporters, or clothing, as the fungus can spread this way.
- If you have athlete's foot - treat it promptly. Always put your socks on before your underwear to help prevent the fungus from spreading from your feet to your groin.
Causes & Triggers
Jock itch is caused by a group of fungi called dermatophytes. These microscopic organisms are naturally present on human skin, but they can multiply and cause an infection under certain conditions. The main trigger for jock itch is a warm, moist environment, which allows these fungi to thrive.
Common triggers include:
- Prolonged moisture: Sweating heavily during exercise or in hot, humid weather and not drying off properly.
- Friction: Tight clothing or underwear can rub against the skin, creating irritation and a favorable environment for fungal growth.
- Sharing contaminated items: Using towels or clothing that have been used by someone with a fungal infection.
- Spreading from other body parts: The fungus from athlete's foot can easily spread to the groin.
People who are most likely to develop jock itch include athletes, individuals who are overweight (due to increased skin folds and sweating), those who sweat profusely, and people with weakened immune systems or conditions like diabetes. While it's more common in men, women can get it too.
When to see a doctor:
It’s a good idea to see a doctor if you're unsure if what you have is jock itch, or if the rash doesn't start to improve after about a week of self-care measures like keeping the area clean and dry. You should also seek medical attention if:
- The rash is very painful, widespread, or spreading quickly.
- You notice signs of a possible bacterial infection, such as pus, significant swelling, warmth, or if you develop a fever.
- The rash keeps coming back despite your best efforts to prevent it.
- You have a weakened immune system or diabetes.
A dermatologist is a doctor who specializes in skin conditions. If your primary care doctor is unsure, or if your jock itch is persistent or severe, they may refer you to a dermatologist for further evaluation and to discuss the best path forward. Remember, getting an accurate diagnosis is key.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
- Is jock itch the same as athlete's foot? They are very similar and caused by the same types of fungi! The main difference is the location: athlete's foot affects the feet, while jock itch affects the groin area. It's quite common for the fungus to spread from the feet to the groin.
- Can women get jock itch? Yes, absolutely. Although it's diagnosed more often in men, women can certainly develop jock itch if the conditions are right for the fungus to grow in the groin area.
- Can jock itch spread to other parts of my body? It can. If you scratch or touch the infected area and then touch another part of your body without washing your hands, you could potentially spread the fungus. This is why handwashing is so important.
- Will jock itch go away on its own without any specific care? It's unlikely to completely resolve on its own. While symptoms might sometimes lessen, the fungus usually needs specific measures to be fully eliminated. Without proper care, it can persist or keep coming back.
- Is jock itch a sign of being unclean? Not at all. While good hygiene (keeping the area clean and dry) is crucial for prevention and management, even very clean individuals can get jock itch. Factors like sweating a lot, wearing tight clothing, or exposure to the fungus in a gym locker room can contribute, regardless of personal cleanliness.
References
- American Academy of Dermatology Association. (n.d.). Jock Itch: Diagnosis and treatment. Retrieved from https://www.aad.org/public/diseases/a-z/jock-itch-treatment
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2021, July 28). Ringworm of the Groin (tinea cruris). Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/fungal/diseases/ringworm/jock-itch.html
- Mayo Clinic. (2022, December 14). Jock itch. Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/jock-itch/symptoms-causes/syc-20353807